UNDER WHOSE COMMAND?
Human rights abuses under Myanmar’s military ruleA report by Security Force Monitor
For the first time, extensive research has mapped the Myanmar Army’s entire Chain of Command. The research details the hierarchy and control exercised by senior commanders over hundreds of units throughout a twelve year period. We now know the entire chain of command and can identify who was in command when each alleged human rights abuse occurred between 30 March 2011 and 30 March 2023.
Proving individual responsibility for war crimes and crimes against humanity is a complex task. This is especially true in Myanmar, where secrecy around the army’s structure has long hampered efforts for accountability.
Since 2011 more than 60% of the senior commanders of the Myanmar Army have had disappearances, killings, rape or torture allegedly committed by units under their command.
A decade of worsening human rights abuses
On 30 March 2011, Min Aung Hlaing became Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of Myanmar, otherwise known as the Tatmadaw. The Myanmar Army is by far its largest and most powerful branch of the armed forces. Since Min Aung Hlaing took command of the military, the United Nations, human rights groups and others have accused the Myanmar Army of committing genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes across the country.
During the same period, Myanmar initially appeared to be on a path towards greater democracy and civic participation. That ended in February 2021. Led by Min Aung Hlaing, the army ousted the democratically-elected government, headed by the National League for Democracy party, in a coup d’état. Civilian protest was met with a wave of violence unleashed by the armed forces. Today, the army is accused of continuing to enact a brutal crackdown including arbitrary arrest, torture, enforced disappearances and mass killings.
A crowd of hundreds of thousands of protestors gather in the centre of Yangon to show their support for the Civil Disobedience Movement and to reject the coup.
The Security Force Monitor (SFM) is a project of the Columbia Law Human Rights Institute. Our new research lays bare the Chain of Command of the Myanmar Army and reveals how allegations against soldiers from low level units can be linked to senior army commanders.
Since 2011 more than 60% of the senior commanders of the Myanmar Army have had disappearances, killings, rape or torture allegedly committed by units under their command.
This research shines new light on the control exercised by senior army commanders over the conduct of individual army units. We hope it can be used to support efforts to deliver accountability for alleged crimes against humanity, war crimes committed by the Myanmar Army, and justice for those that have suffered at their hands.
![]()
Military commanders take their positions in parliament. The Pyithu Hluttaw, or lower house of Myanmar’s parliament, is dominated by former soldiers, their positions guaranteed under a constitution which was ratified after a fraudulent referendum in 2008.
Methodology
Establishing the chain of command is one of the key elements in determining who should be held accountable for war crimes or crimes against humanity.
The Myanmar Army is one of the most secretive and opaque militaries in the world. Without a good understanding of the structure of the Myanmar Army, human rights groups have struggled to link alleged violations committed by low-level units to the generals in charge.
To build our research we relied on open source information drawn from the work of national and international human rights organizations and local activists. In doing so, we have been able to piece together the most comprehensive picture of the army’s operational structure to date.
Our sources include books, independent newspapers and the military’s own media outlets. We rigorously tracked what each of these sources reported about every unit and commander over the course of more than twelve years to build our picture of the army, piece by piece:

For example a commander is identified in a single newspaper article. This establishes a single claim for the commander on the day the article was published.
As we find more sources with claims about the commander at different points in time, we add them to the timeline.
We can now see a fuller timeline of the commander’s career.
The secrecy around the Myanmar Army means there is a lot of conflicting information in the public domain. Every time we get a new source we analyze it against everything else in our dataset.
Sometimes sources might have competing claims about who is the commander of a unit.
We can resolve the conflict and identify the accurate information by comparing sources about each person’s career, as well as data on similar commanders.
We used this basic cross referencing approach with our research on the chain of command, commanders, the areas under the commander’s control and all other aspects of our dataset.
![]()
Armed Forces Day. 15,000 soldiers paraded in an annual event that is recognised as the day the modern Burmese army was founded. Panos
Myanmar’s Army
The Myanmar Army has a dynamic structure that changes depending on where units are operating. Our research builds on this understanding to show how command flows from top to bottom.
At the top is the Commander-in-Chief of Defense Services, Min Aung Hlaing, who controls all branches of the military. Under him is Soe Win, simultaneously Deputy Commander-in-Chief of Defense Services and commander of the Myanmar Army. Both have held their positions since 30 March 2011.
Below them is the Joint Chief of Staff who controls all aspects of the army, including the General Staff of the army and six Bureaus of Special Operations.
Each Bureau of Special Operations controls at least one Regional Military Command (RMC).
The people that hold these positions are the senior commanders of the Myanmar Army sitting at the top of the army’s hierarchy.
Below these senior commanders are units which carry out operations on the ground based on orders from these senior commanders.
Two major formations that move around the country are Military Operations Commands (MOCs) and Light Infantry Divisions (LIDs). They fall under the control of the Regional Military Command responsible for the area where they are operating, but also report up to the army chief of staff. RMCs control any army units that enter into their territory.
All Regional Military Commands, Military Operations Commands and Light Infantry Divisions command Infantry and Light Infantry Battalions, which are the main combat unit of the Myanmar Army. This analysis is limited to connecting violations allegedly committed by MOCs and LIDs and these battalions to the wider chain of command.
While this basic structure was known, the specific chain of command for each unit and how it may have changed through time was not. Our research has tracked the movements of every single unit, its command relationship in these three formations, and the careers of senior army commanders for an entire twelve year period.BATTALIONS(LIDS)100xBATTALIONS (MOCS)200xBATTALIONS (ROCS)36xBATTALIONS (RMCS)187xTACTICAL OPERATIONS COMMANDS (LIDS)30xTACTICAL OPERATIONS COMMANDS (MOCS)60xLIGHT INFANTRY DIVISIONS (LIDS)10xMILITARY OPERATIONS COMMANDS (MOCS)20x6xREGIONAL OPERATIONS COMMANDS (ROCS)4x41xTACTICAL OPERATIONS COMMANDS (RMCS)MILITARY REGIONS (YANGON RMCS)REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDS14xBASED ON AREAARMY CHIEF OF STAFFBUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS6xJOINT CHIEF OF STAFFTATMADAW-KYIARMYDEPUTY COMMANDER-IN-CHIEFOF DEFENCE SERVICESTATMADAWCOMMANDER-IN-CHIEF
Understanding this dynamic and changing structure enables us to reveal, for the first time, which senior commanders were in command for every alleged human rights abuse committed by an army unit.
Military and police beat a family arrested during a protest in Mandalay, Myanmar, in 2021.
Chain of Command
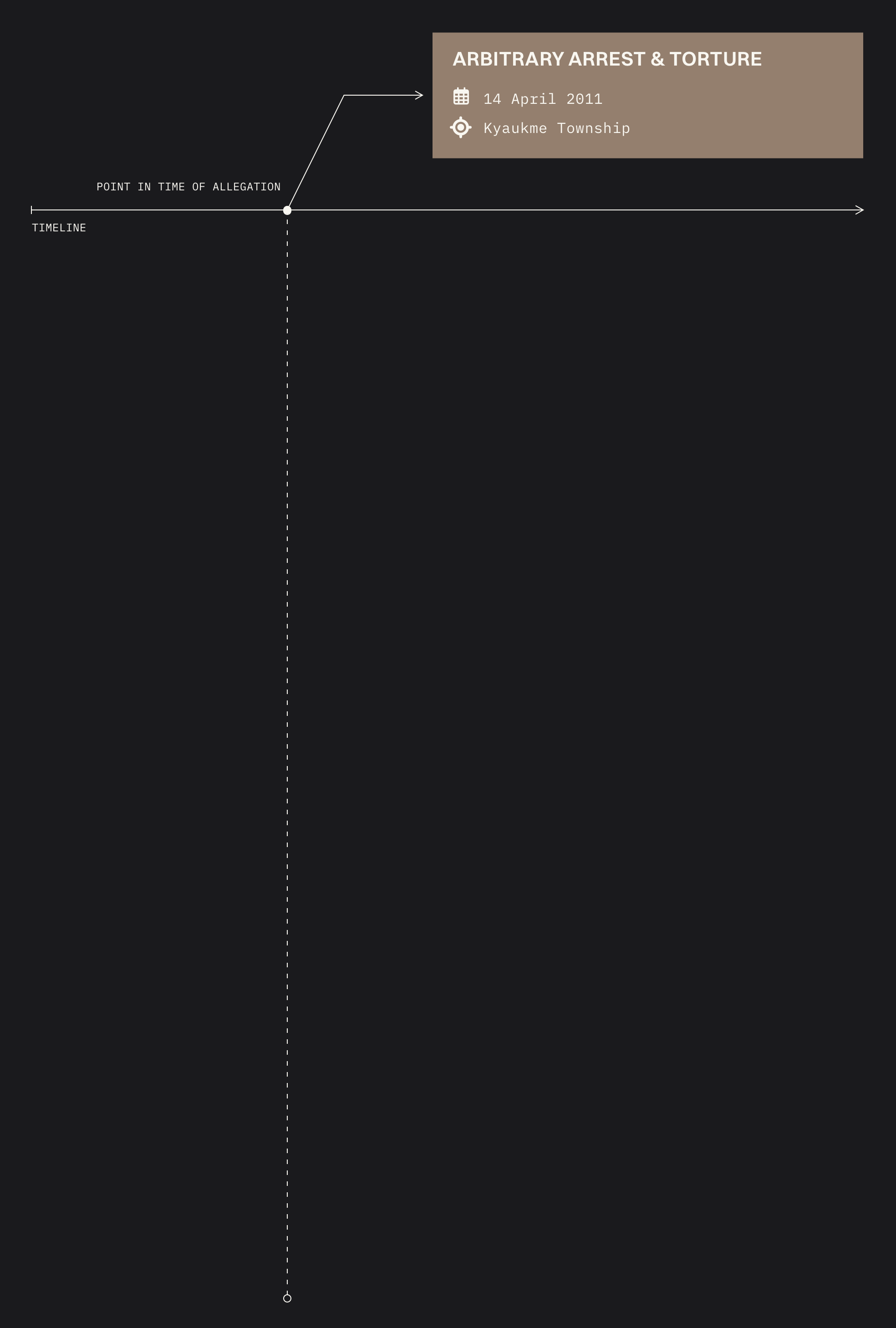
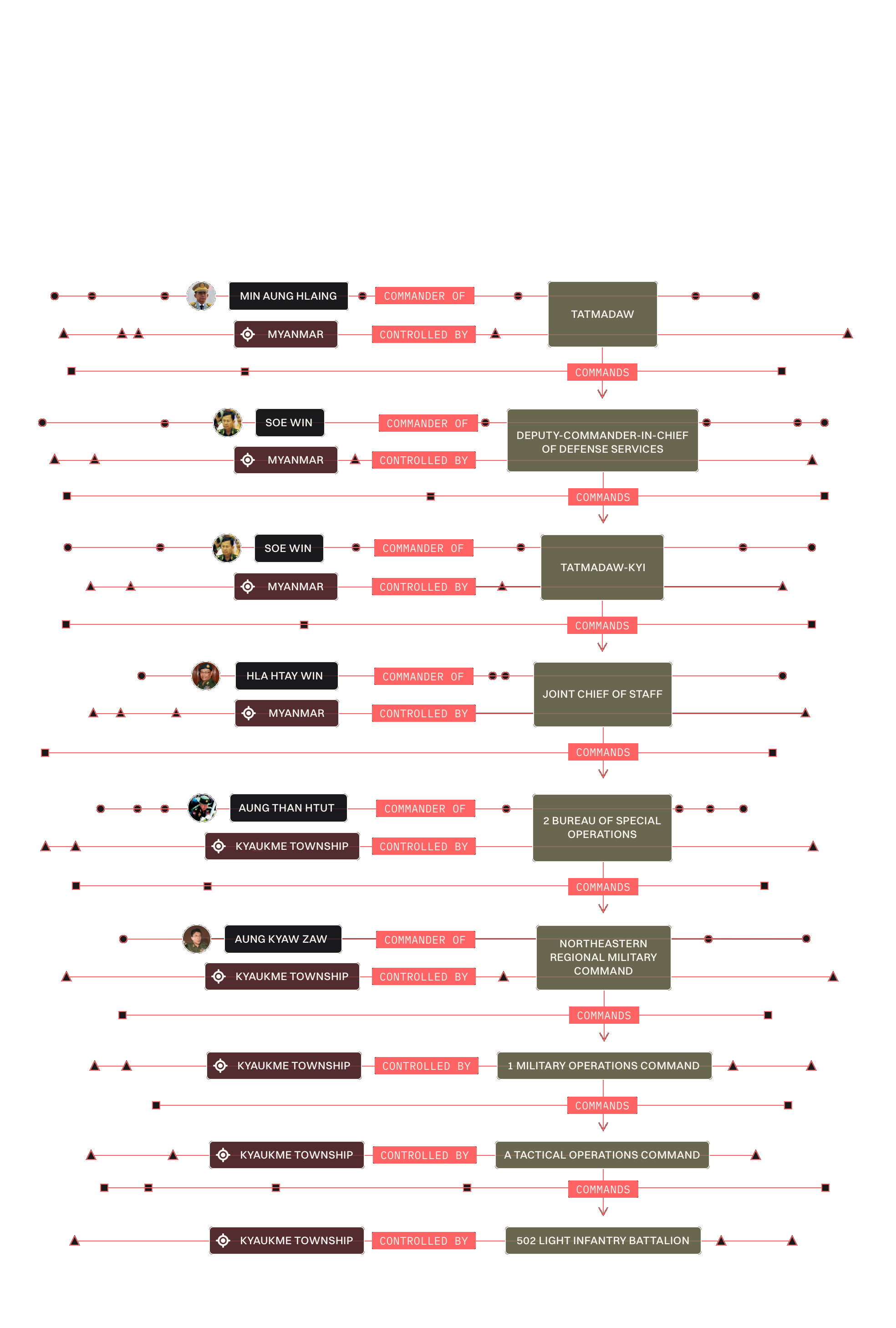
Take this example of allegation of arbitrary arrest and torture in April, 2011, shortly after Min Aung Hlaing became Commander-in-Chief of the military.
The allegation identifies that the 502 Light Infantry Battalion falls under the command of 1 Military Operations Command. Given the date and location more connections can be made to the wider army chain of command.
Sources before and after the alleged violation establish Northeastern Regional Command controls Kyaukme township and the chain of command up all the way to the top of the military.
Other sources from before and after the alleged violation identifies every commander in the chain of command ending with Min Aung Hlaing at the top.

![]()
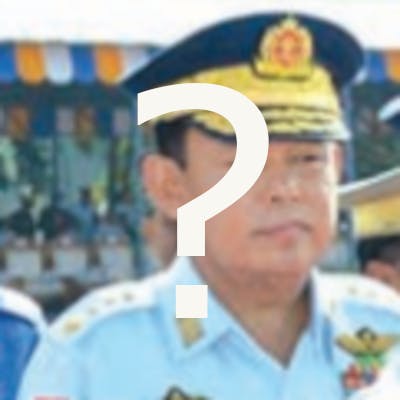
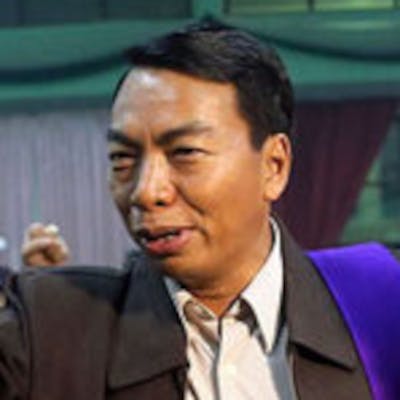
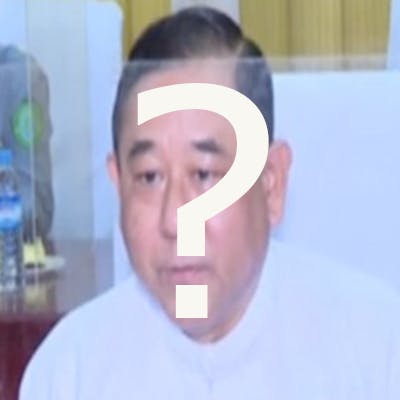
Senior commanders in the Myanmar Army. From left to right: Mya Htun Oo, Soe Win, Min Aung Hlaing.
Linking Allegations
The vast majority of senior army commanders over a twelve year period can be linked through the chain of command to allegations of disappearances, killings, rapes and torture.
Most of these commanders were promoted to higher ranks after these alleged violations occurred.
Since Min Aung Hlaing became Commander-in-Chief of the Myanmar Army in 2011, the entire vast army apparatus was controlled by just 79 senior commanders.
Senior commanders can be held responsible for human rights abuses committed by their subordinates.
64% (51 of the 79) senior army commanders that have served under Min Aung Hlaing have had alleged disappearances, killings, rape or instances of torture committed by units under their command.
54% (28 of 51) of these commanders were promoted in rank after at least one alleged disappearance, killing, rape or instance of torture was committed by units under their command. The others could not be promoted in rank further (9), promotions could not be determined (11), or may be promoted in the future (3).
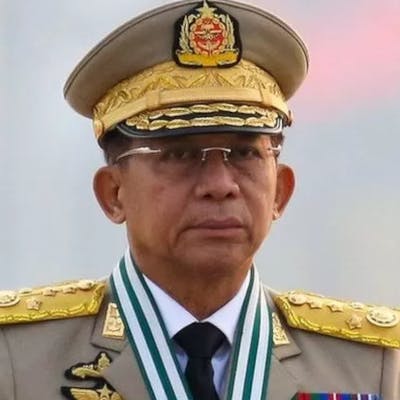
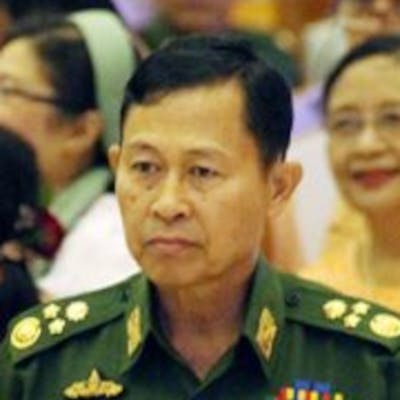
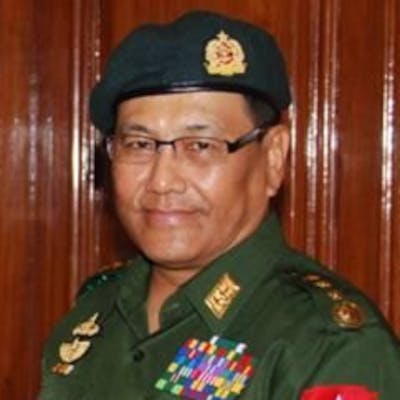
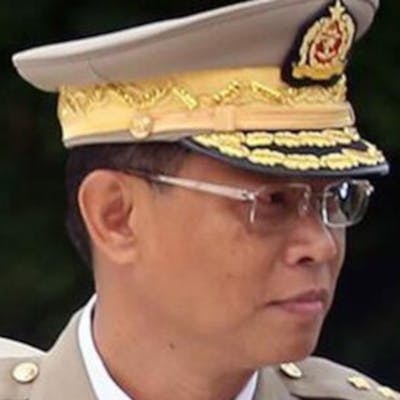
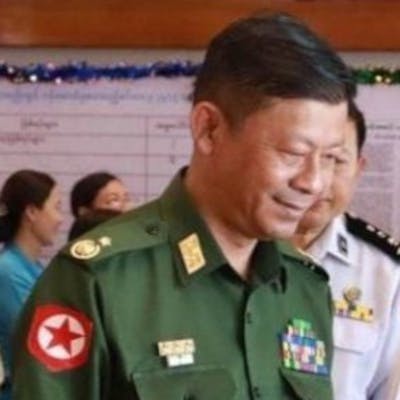
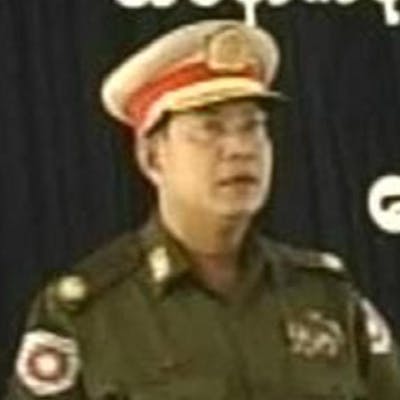
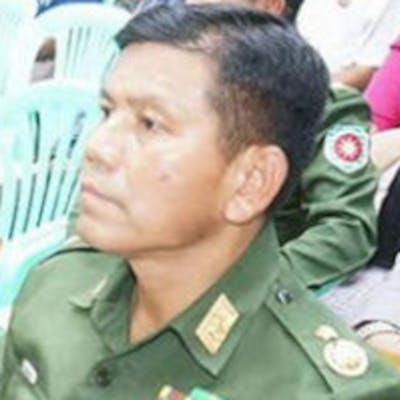
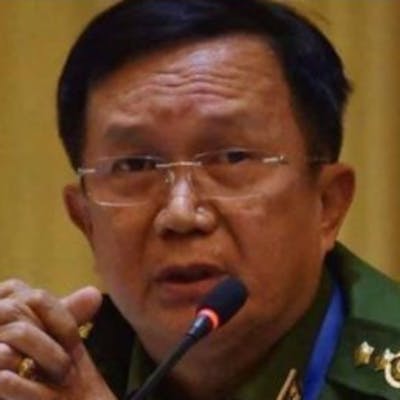















































































Children, affected by clashes between the military and ethnic rebel groups, playing at the Kho Lone monastery, temporarily being used as a camp for Internally Displaced Persons (IDP), in Kutkai in Shan State. Local civil society organisations say more than 2,000 people have been displaced as residents caught in the middle seek safety in nearby monasteries.
Establishing patterns
With a full understanding of the Myanmar Army’s chain of command, we can now map allegations of abuse onto this structure to establish patterns.
Between 30 March 2011 and 30 March 2023, allegations of disappearances, killings, rape or torture have been made consistently against the same units – even when different people were in command.
Over those twelve years, senior army commanders served in multiple different positions.
Whenever commanders served along Myanmar’s borders they almost always had allegations against units under their command. However, when commanding units in major cities like Yangon or the capital Naypyidaw, especially before the 2021 coup, there were no reports of allegations against their subordinate units.
Mya Htun Oo’s career can serve as an example for this analysis. He served in five different positions in the army’s chain of command between 2011 and 2023.

This chart highlights the positions that Mya Htun Oo held in the Myanmar Army between 30 March 2011 and 30 March 2023.
The other circles represent another person who commanded the same unit at some point during that time frame. For example, Eastern Central RMC had nine different commanders, including Mya Htun Oo.
For some positions subordinates units under Mya Htun Oo were accused of committing disappearances, killings, rapes or torture. During other commands there were no such allegations against subordinates.
The same is true for other senior commanders.
Four commanders of Eastern Central RMC, including Mya Htun Oo, had subordinates accused of committing disappearances, killings, rapes or torture during their command.
The other five other commanders of Eastern Central RMC did not have any of those allegations made against units under their control during their command of Eastern Central RMC.EASTERN CENTRAL REGIONALMILITARY COMMAND5 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS
6 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS
GENERAL ARMY STAFF
JOINT CHIEF OF STAFF
This chart shows, for the first time, every position held by every senior commander and whether disappearances, killings, rape or instances of torture were allegedly committed by units under their command for that position.
In many areas of the country, almost every single person who ever held command had disappearances, killings, rape or instances of torture allegedly committed by units under their command.
This is particularly true in areas of long-standing conflict and concern for human rights abuses: Kachin state controlled by Northern RMC, Kayin state controlled by Southeastern RMC, and Shan state divided among Northern, Eastern Central, Eastern, Northeastern, and Triangle RMCs.NAYPYIDAW REGIONALMILITARY COMMANDYANGON REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDSOUTHEASTERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDCOASTAL REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDSOUTHERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDSOUTHWESTERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDWESTERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDEASTERN CENTRAL REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDEASTERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDNORTHEASTERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDTRIANGLE REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDCENTRAL REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDNORTHERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDNORTHWESTERN REGIONAL MILITARY COMMANDGENERAL ARMY STAFF6 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS5 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS4 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS3 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS2 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONS1 BUREAU OF SPECIAL OPERATIONSJOINT CHIEF OF STAFFTATMADAW-KYIARMYDEPUTY COMMANDER-IN-CHIEFTATMADAW COMMANDER-IN-CHIEF
This report
Our research is ongoing. We are continually adding to our dataset. The facts and statistics in this report were last updated on 11/1/2023
As noted throughout the text, this analysis is limited to particular allegations against specific units. This analysis does not include allegations where no specific unit is identified. A future analysis will include these types of allegations. The analysis does not include allegations against artillery, armored or support units of the army, as the chain of command research for these units is ongoing.
For the most up to date information, please get in touch.
Search the chain of command
You can search the chain of command in Myanmar for yourself.
Explore the connections through the chain of command from alleged violations up to senior commanders in our Data Explorer.
Learn more about how we did this research
Go to the About section to learn more about specific areas of Security Force Monitor’s methodology in researching the Myanmar Army.